
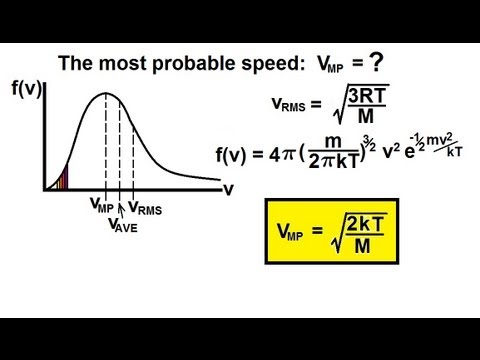
The equation is exactly the same in terms of the Kelvin temperatures as in terms of the Celsius temperatures. After leaving the freezer, the vapour returns to the compressor, where it is, of course, compressed (which is why the pump is called the compressor).Assuming that the final temperature lies between 0 C (273 K) and 100 C (373 K), the heat balance equation in terms of temperatures in centigrade degrees is: In our tool, we added two formulae for work: The simplest work force × distance expression and The velocity change equation based on the formula for kinetic energy.
THERMODYNAMICS CALCULATOR PHYSICS HOW TO
A fan may also distribute the cooled air throughout the rest of the refrigerator. How to use the work calculator Use our work calculator to quickly estimate the work in physics based on two different methods.

It is then forced through a nozzle into a system of wider pipes (the evaporator) surrounding the freezer, and there it vaporizes, taking heat from the food and from the air in the freezer. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules in the system. Click a folder name to view files in that folder.
THERMODYNAMICS CALCULATOR PHYSICS ARCHIVE
Shortly before the fluid reaches the freezer it is in liquid form, moving along some rather narrow pipes. TI-83/84 PLUS BASIC SCIENCE PROGRAMS (OTHER PHYSICS) Archive Statistics Click a filename to download that file.
The fluid is forced around a system of tubes by a pump called the compressor. The exact formula or mixture is doubtless a trade secret. The science of heat, temperature, work, pressure, entropy, enthalpy.all governed by. the already negative image of thermodynamics held by the average student. The chlorofluorocarbons have been largely replaced by hydrofluorocarbons, such as C 2H 2F 4, which are believed to be less damaging to the ozone layer. Online calculators for thermodynamics and statistical mechanics. Yet, all the physicists behind the laws of thermal science had only this tool. Calculate the pressure-volume work done by the system when the gas expands from 1-litre to 2-litre against a constant external pressure of 10 atmosphere. “Freon”, which was a mixture of chlorofluorocarbons, such as CCl 2F 2, was in fashion for a while, but escaping chlorofluorocarbons have been known for some time to cause breakdown of ozone (O 3) in the atmosphere, thus destroying our protection against ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. In industrial refrigerators, the refrigerant may be ammonia, but this is considered to be too dangerous for domestic use. The fundamental principles described in this section do, of course, still apply in the real world! In a real refrigerator, the working substance (the refrigerant) is a volatile fluid which is vaporized in one part of the operation and condensed to a liquid in another part. As mentioned elsewhere in this course, I am not a practical man and I am not suited to describing real, practical machines. Of course the working substance in a real refrigerator (“fridge”) is not an ideal gas, nor does one follow a Carnot cycle – there are too many practical difficulties in the way of achieving this ideal dream. This, of course, can be much greater than 1 – but no refrigerator working between the same source and sink temperatures can have a coefficient of performance greater that that of a reversible Carnot refrigerator. If the piston compresses the gas as it is moved inward, work is also donein this case, on the gas. If the gas expands against the piston, it exerts a force through a distance and does work on the piston. 1 shows a gas confined to a cylinder that has a movable piston at one end. Therefore the coefficient of performance for a Carnot refrigeration cycle can be calculated from Then how does a thermodynamic system do work Figure 3.3. \]īy the first law of thermodynamics, the denominator of the expression is Q 2 − Q 1, and for a reversible Carnot cycle, the entropy in equals the entropy out, so that Q 2/ Q 1 = T 2/ T 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
